Here you will be introduced to the terminology of astrology in order to
comprehend the system. The astronomy, relevant
to predictive astrology, will be discussed in the first place.
ASTRONOMICAL TERMINOLOGY
ECLIPTIC: The Ecliptic is the
apparent path of the Sun.
ZODIAC & ASTROLOGY:
The Zodiac is an imaginary belt in the heavens extending to 9º on both sides of ecliptic containing 12 signs of 30º each. The first sign starts from 0º of the sign Aries (Mesha) and extends to 30º. Each degree can be divided into 60 minutes, and each minute can be divided into 60 seconds for the purpose of precision in calculations.
From the earth, the signs appear to be moving in a clockwise motion. The earth has two revolutions: one around the Sun which is completed in 365.25 days, and the other around its own axis which is completed in 24 hours. Due to earth's movement around the Sun, when the Sun is viewed in the background of the zodiac it appears from the earth that the Sun moves/rotates at the speed of 1º per day in an anti-clockwise direction.
The revolution of the earth around its own axis causes rise of all the twelve signs in the eastern horizon in a period of 24 hours.
The zodiac is also divided into 27 nakshatras (constellations) consisting of groups of fixed stars.
EQUINOX:
The Equinox is the time when the Sun apparently crosses the equator and the day and the night are equal. It is believed that when the Sun touches its equinoctial point of zero degree of Aries, the earth moves westward with reference to a particular constellation. The zodiac seen or measured from the beginning of Aries from the westward moving equinoctial point is known as a moving or tropical zodiac. When zero degree of Aries is reckoned from a particular star, the same is known as a fixed or sidereal zodiac. The Vedic system of Astrology uses the concept of fixed zodiac and that is why the Sun enters Aries almost on identical dates every year. In the Vedic system of Astrology, when we are speaking of various signs we are actually speaking about the fixed constellations with the same name. The Vedic system of Astrology is known as Nirayana System.
AYANAMSA:
The ayanamsa is the distance between the fixed and the moving zodiacs.
SOLAR TIME:
We measure time based on the concept of the solar day. It is defined as an average time period of the successive passages of the Sun over a given meridian. It is exactly 24 hours and is known as the mean solar day.
SIDEREAL TIME:
The time required for a 360 degree rotation of the earth around its axis, causing a given star in the sky to return to the same position in relation to the earth is known as the sidereal day and this period is about 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds.
ASCENDANT/ASCENDING SIGN/LAGNA
The ascendant or lagna is that point in the zodiac which rises at the time of birth of a person with reference to the place of birth. The position of planets in the zodiac is noted with reference to the earth.
The ascendant is the first house in a horoscope and the rest of the houses are reckoned from it. The ascendant is an important part of the horoscope and it helps in identifying the functional nature of planets. It also helps in analyzing the transit impact of planets.
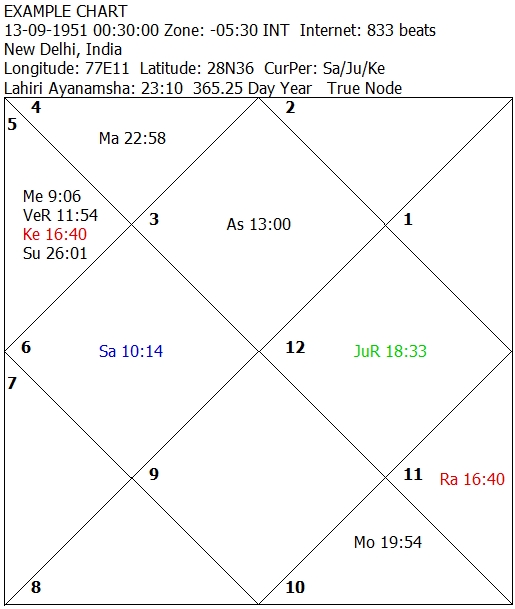
In the example chart the house where sign No.3 is written is the Ascendant. Sign No. 3 means Gemini. The rising degree in the ascendant is 13. The next house counted anti clock-wise containing sign No. 4 is the second house. The sign No. 4 means Cancer.
IMPORTANCE OF ASCENDANT/ASCENDING SIGN/LAGNA:
The functional nature of the planets in a birth chart is identified through the ascendant. The functional nature helps in identifying the strength of planets as well as the planets which cause unfavorable influences in the birth chart. The ascendant helps us in identifying the strong aspects of life as well as those aspects of life under stress, including health. The astrological remedial measures for various life problems are recommended on the basis of the functional nature of the planets.
PLANETARY LONGITUDES:
Planetary longitude is the angular distance measured eastward on the ecliptic from the starting point of the fixed zodiac and it gives the apparent position of the planet in a particular sign at a given time.
LONGITUDE:
Longitude is the angular distance of any place on the earth’s surface, east or west of a standard meridian (e.g. that of Greenwich), measured in degrees up to 180º east or west, or in units of time (1 hour = 15º). With the help of the longitude of a particular place with reference to Greenwich (0º), we calculate the local mean time for that place. As the earth rotates from west to east (anti-clockwise), those places east of Greenwich will be ahead of Greenwich Time and those to the west will be behind Greenwich Time. For each degree of longitude, there is a difference of four minutes in time.
LATITUDE:
Latitude is the angular distance on its meridian of any place on the earth’s surface from the equator. It is measured in degrees and minutes from the equator towards either the North Pole or South Pole. The equator represents 0 degree latitude. Latitudes are thus imaginary lines drawn parallel to the equator.
Note: Even if you find understanding astronomical terms difficult, you can still proceed with further study. The lack of clear understanding of the astronomical terminology will not create hurdles in your understanding of the Predictive Astrology.
Predictive Astrology and Astronomy are two different sciences. Predictive Astrology is based on Astronomy, but the deep knowledge of Astronomy is not at all necessary for predictive analysis.
NATAL CHART/BIRTH HOROSCOPE:
Natal chart, radical chart, horoscope or natal positions are the positions of the ascendant and planets in various signs as noted at the time of birth. Natal positions, therefore, are fixed. The planetary positions noted with reference to a particular chart for subsequent periods are known as transit or transit positions.
See the example chart above which is called a natal chart.
PLANETARY CONJUNCTION:
Conjunction is the apparent coincidence or proximity of two or more celestial objects as viewed from the earth. A conjunction can be exact or close. If the difference in longitudes happens to be less than one degree, the resulting conjunction is known as an exact conjunction. If the difference in longitudes is within five degrees, the same is known as a close conjunction. In the example chart above Mercury and Venus are in close conjunction.In the example chart above Mercury and Venus are in close conjunction.
PLANETARY ASPECTS:
The aspects are partial and full. In the Vedic system of astrology, we are concerned with only full aspects. Each planet is believed to aspect fully the seventh house from where the planet is residing. Thus the seventh house is counted from the placement of the planet, including the house it resides in.
In addition to the seventh aspect, planets posited outside the orbit of the earth (Mars, Jupiter and Saturn) as well as Rahu and Ketu have additional special full aspects as follows:
a) Saturn
aspects the third and tenth houses from its location.
b) Mars aspects the fourth and eighth houses from
its location.
c) Jupiter, Rahu and Ketu aspect the fifth and
ninth houses from their location.
In the example chart Mars in the second house and the Moon in the eighth house mutually aspect each other closely as their aspecting longitudinal difference is less than five degrees. Mars is at 22 deg 58 minutes while the Moon is 19 deg and 54 minutes. The difference between these two (22 deg 58 minutes - 19 deg 54 minutes) is 3 degrees and four minutes.
Planets influence other houses/planets aspected by them favorably or unfavorably, depending upon their functional nature in the horoscope. The principle of exact or close aspect is identical to exact or close conjunction i.e. when a planet casts its aspect on another planet(s) or on the most effective point of house(s) within an orb of one degree, the aspect is known as an exact aspect. If the difference in planetary longitudes is within five degrees, then the aspect is known as a close aspect.
WIDE CONJUNCTION OR ASPECTS:
The conjunctions or aspects with more than five degrees of longitudinal difference are wide conjunctions or aspects. These do not have a permanent impact in life except for short lived transit influences on the planets involved in wide conjunctions or aspects. The wide aspects give their results in the latter part of life, say around 60 years or after.
The aspect of a functional benefic planet will be effective corresponding to the strength of the planet(s)/house(s) involved. If the aspecting functional benefic planet is weak due to any reason including debilitation, its effectiveness will be weak and limited, but its close aspect will always act as a helping force.
The close aspect of a functional malefic planet, except on the most effective point of its mooltrikona house, will always act as a damaging force.